Embarking on a linguistic journey, we delve into the world of pengertian mashdar, a grammatical concept that plays a pivotal role in the Arabic language. Mashdar, meaning “source” or “origin,” is a verbal noun that captures the essence of an action, providing a versatile tool for expressing various shades of meaning.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will unravel the intricacies of mashdar, exploring its types, grammatical properties, and diverse applications in Arabic literature and language learning. By the end of this exploration, you will have gained a profound understanding of this fundamental linguistic element, empowering you to navigate the complexities of Arabic with confidence.
Definition of Mashdar
A mashdar is a verbal noun in Arabic grammar that denotes the infinitive form of a verb. It is derived from the word “ṣadr,” which means “chest” or “source,” and indicates the origin or source of an action. Mashdars are used to express the general concept of an action without specifying its subject or tense.
Etymology of Mashdar
The term “mashdar” comes from the Arabic root “ṣ-d-r,” which has the primary meaning of “to issue forth” or “to emanate.” In the context of grammar, a mashdar is considered the source or origin of a verb, as it represents the infinitive form that encompasses all potential subjects and tenses.
Examples of Mashdar in Arabic
In Arabic, mashdars are typically formed by adding the prefix “mi-” to the beginning of the verb’s root. For example:
- The mashdar of the verb “kataba” (to write) is “miktabah” (writing)
- The mashdar of the verb “qara’a” (to read) is “qira’ah” (reading)
- The mashdar of the verb “takallama” (to speak) is “takallam” (speech)
Mashdars can also be formed using other prefixes, such as “ma-” or “si-,” depending on the verb’s pattern.
Types of Mashdar
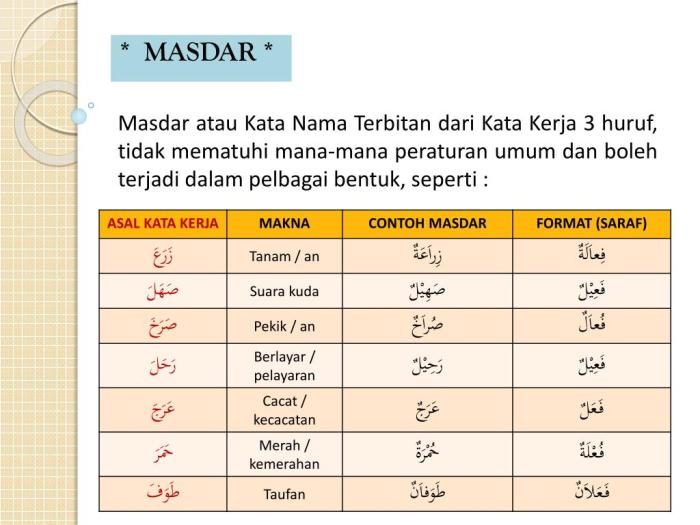
Mashdars can be classified into different types based on their formation and function. The two main types of mashdars are isim mashdar and masdar mi’i.
Isim Mashdar, Pengertian mashdar
Isim mashdar, also known as the nominal mashdar, is a noun derived from a verb that denotes the action or state expressed by the verb. It is formed by adding the prefix “ism” to the root of the verb. For example, the isim mashdar of the verb “kataba” (to write) is “kitabat” (writing).Isim
mashdars have the following characteristics:* They function as nouns.
- They can take on the grammatical case of a noun.
- They can be used as the subject, object, or complement of a sentence.
Masdar Mi’i
Masdar mi’i, also known as the verbal mashdar, is a verbal noun that denotes the action or state expressed by the verb. It is formed by adding the suffix “-an” to the root of the verb. For example, the masdar mi’i of the verb “kataba” (to write) is “kitaban” (writing).Masdar
mi’is have the following characteristics:* They function as verbs.
- They can take on the grammatical tense and mood of a verb.
- They can be used as the main verb of a sentence.
Grammatical Properties of Mashdar
Mashdar holds a significant position in Arabic grammar, exhibiting unique syntactic and morphological characteristics that distinguish it from other parts of speech.
Syntactically, mashdar can function in various roles within a sentence:
- Subject:Mashdar can act as the subject of a sentence, denoting an action or state that is being discussed.
- Object:Mashdar can serve as the direct or indirect object of a verb, indicating the purpose or result of an action.
- Complement:Mashdar can complement a verb or adjective, providing additional information about the action or quality being described.
Morphologically, mashdar follows specific derivational patterns. The most common pattern involves adding the suffix “-an” to the root of a verb, resulting in a noun-like form that retains the verbal meaning. For example, the verb “kataba” (to write) forms the mashdar “kitaban” (writing).
Use of Mashdar in Arabic Literature
Mashdar has been an integral part of Arabic literature, employed effectively by both classical and modern writers. Its unique ability to capture the essence of actions and states has made it a versatile tool for literary expression.In classical Arabic literature, mashdar was frequently used in poetry and prose to convey a wide range of emotions and ideas.
Poets such as al-Mutanabbi and al-Ma’arri utilized mashdar to express themes of love, loss, and philosophical contemplation. In prose, writers like al-Jahiz and Ibn al-Muqaffa employed mashdar to narrate historical events and convey moral lessons.Modern Arabic literature has continued the tradition of using mashdar, albeit with some notable stylistic shifts.
Contemporary writers such as Naguib Mahfouz and Tayeb Salih have incorporated mashdar into their narratives to explore themes of identity, social change, and the human condition. Mashdar’s ability to convey both the concrete and abstract has made it an indispensable tool for modern Arabic writers seeking to capture the complexities of human experience.
Stylistic and Rhetorical Functions of Mashdar
Mashdar serves various stylistic and rhetorical functions in Arabic literature, including:
Conciseness
Mashdar, or infinitive in English, is a verbal noun that expresses the meaning of an action or state. In Islamic practices, understanding mashdar is crucial for comprehending the various forms of dhikr (remembrance of God). To learn more about the proper way to perform dhikr, refer to the comprehensive guide: Cara Berzikir Sesuai Ketentuan: Panduan Lengkap . This guide covers the different types of dhikr, their meanings, and the appropriate times and occasions for each.
By understanding mashdar and following the guidelines in this guide, one can enhance their dhikr practices and deepen their connection with God.
Mashdar allows writers to convey actions and states in a concise and efficient manner, avoiding the need for lengthy verbal constructions.
Emphasizing the Action
Mashdar places emphasis on the action or state itself, rather than the agent performing it. This can be used to highlight the significance of the action or to create a sense of immediacy.
Figurative Language
Mashdar can be used as a figure of speech, such as a metaphor or metonymy, to create vivid imagery and evoke emotions.
Rhetorical Effect
Mashdar can be employed to create a particular rhetorical effect, such as persuasion, argumentation, or emotional appeal.In addition to these functions, mashdar can also be used to create rhythm and flow in literary works, contributing to the overall aesthetic appeal of the text.
Mashdar in Language Learning: Pengertian Mashdar
Understanding mashdar is crucial for Arabic language learners as it provides a comprehensive understanding of the language’s verbal system and plays a vital role in various grammatical constructions.
To facilitate effective teaching and learning of mashdar, consider the following tips and strategies:
Teaching Mashdar
- Introduce mashdar as a verbal noun that captures the action or state expressed by the verb.
- Emphasize the importance of recognizing the different patterns used to form mashdars (e.g., fa’l, maf’ūl, ṣifat al-maf’ūl).
- Provide ample examples and exercises to illustrate the usage of mashdars in various grammatical contexts.
Learning Mashdar
- Regularly practice identifying and forming mashdars from different verb forms.
- Pay attention to the patterns and rules governing mashdar formation.
- Utilize flashcards or other memory aids to enhance memorization and recall.
Mashdar and Verb Patterns
Mashdars are closely related to verb patterns in Arabic. Each verb pattern has a corresponding mashdar that shares the same root and meaning.
The following table illustrates the relationship between verb patterns and their corresponding mashdars:
| Verb Pattern | Mashdar | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| فعل | فعل | Action |
| انفعل | انفعال | Passive action |
| تفاعل | تفاعل | Mutual action |
| استفعل | استفعال | Seeking or requesting an action |
| افتعل | افتعال | Pretending or making something appear to be |
Mashdar and Noun Forms

Mashdar shares several similarities and differences with other noun forms in Arabic. Understanding these similarities and differences is crucial for effective usage.
Mashdars, like other nouns, can function as subjects, objects, or complements in a sentence. They can also be modified by adjectives and prepositions.
In linguistic terms, a mashdar is a verbal noun that expresses the meaning of an action or state without specifying its tense or subject. Understanding this concept is crucial for comprehending the nuances of language. To further delve into the practical applications of this knowledge, we can explore the article Cara Mengolah Hasil Panen: Teknik Persiapan dan Metode , which provides valuable insights into the techniques and methods used in crop processing.
This will not only enhance our understanding of mashdars but also provide practical knowledge in a related field.
Similarities
- Both can function as nouns:Mashdars and other noun forms can act as nouns, representing actions, objects, or concepts.
- Modifiable by adjectives and prepositions:Both mashdars and other nouns can be modified by adjectives to describe their qualities and by prepositions to indicate their relationships with other words in the sentence.
Differences
- Verbal nature:Mashdars retain a verbal aspect, indicating an action or state, while other nouns do not.
- Derivation:Mashdars are derived from verbs, while other nouns can be derived from various sources, including adjectives, adverbs, and particles.
- Specific patterns:Mashdars follow specific patterns based on the verb form they are derived from, while other nouns do not have such patterns.
Despite these differences, mashdars and other noun forms play essential roles in Arabic grammar and are used extensively in literary and spoken Arabic.
Mashdar and Adverbial Forms

Mashdar can also function as an adverbial form in Arabic, conveying adverbial meanings such as manner, time, and place.
When used as an adverb, mashdar typically appears in the accusative case, and it often takes on a specific preposition to indicate the intended adverbial meaning.
Manner
- Mashdar in the accusative case with the preposition bi-(with) expresses manner.
- For example, the mashdar kitābah(writing) in the accusative case with bi-( bi-kitābah) means “in writing” or “by writing.”
Time
- Mashdar in the accusative case with the preposition fi-(in) expresses time.
- For example, the mashdar dukhūl(entering) in the accusative case with fi-( fi-dukhūl) means “upon entering” or “at the time of entering.”
Place
- Mashdar in the accusative case with the preposition ilā-(to) expresses place.
- For example, the mashdar madrasah(school) in the accusative case with ilā-( ilā-madrasah) means “to school” or “towards school.”
Mashdar and Semantic Roles
Mashdar can play various semantic roles in Arabic sentences, representing actions, states, or events.
As a noun, mashdar can function as a subject, object, or complement. It can also express abstract concepts, qualities, or attributes.
Mashdar as Action
- Mashdar can represent an action or process, similar to a verb.
- Example: “الكتابة” (writing) represents the action of writing.
Mashdar as State
- Mashdar can express a state or condition.
- Example: “الحزن” (sadness) represents the state of being sad.
Mashdar as Event
- Mashdar can refer to an event or occurrence.
li>Example: “الموت” (death) represents the event of dying.
Final Summary
In conclusion, pengertian mashdar serves as a cornerstone of Arabic grammar, offering a nuanced and expressive means of conveying actions, states, and events. Its versatility extends beyond linguistic boundaries, enriching literary works with stylistic and rhetorical depth. Understanding mashdar empowers language learners to delve deeper into the intricacies of Arabic, unlocking its expressive potential.
Essential FAQs
What is the etymology of the term “mashdar”?
The term “mashdar” originates from the Arabic root “sh-d-r,” which means “to flow” or “to emanate.” This root captures the idea of mashdar as a source or origin of an action.
How is mashdar used in Arabic literature?
Mashdar plays a significant role in Arabic literature, particularly in classical poetry and prose. It is employed for its stylistic and rhetorical value, adding depth and nuance to literary expressions.
Why is understanding mashdar important for Arabic language learners?
Grasping mashdar is crucial for Arabic language learners as it provides a deeper understanding of Arabic grammar and enhances their ability to comprehend and produce grammatically correct sentences.

